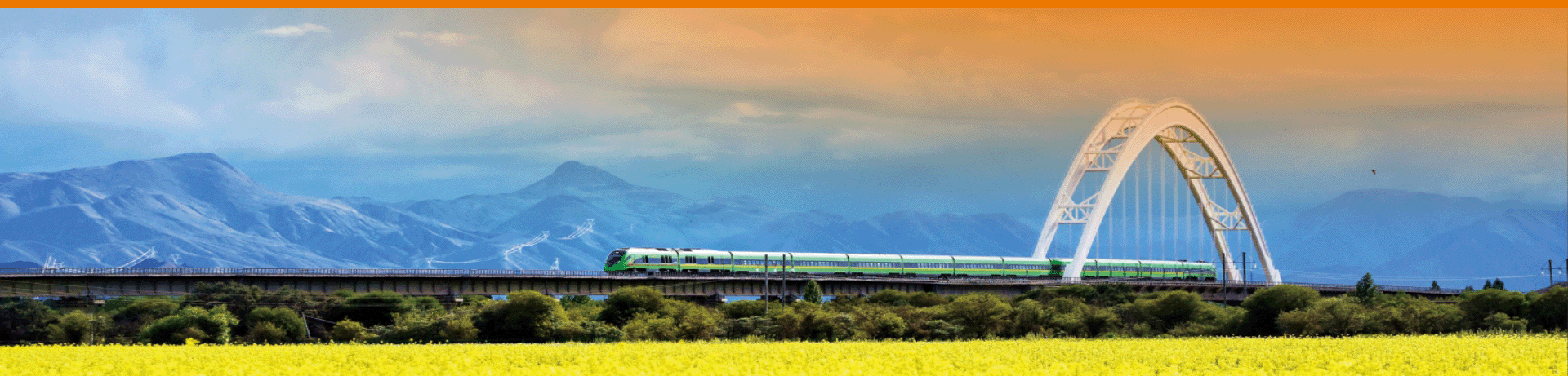




Strengthen Infrastructure Development in All Aspects
Xizang prioritizes infrastructure development as a crucial task and prerequisite for advancing high-quality growth. Its efforts include swiftly building a comprehensive three-dimensional transportation network that integrates railways, highways, and aviation and expediting the development of key infrastructure like water conservancy, energy, and new facilities, aiming to establish an increasingly robust foundation for high-quality development.
Achieve extraordinary development in transportation facilities
The Xizang Autonomous Region actively establishes a main framework of the highway network characterized by "four vertical lines, three horizontal lines, and eight transport corridors", initially creating vital routes connecting four domestic provinces (region)—Sichuan, Yunnan, Qinghai, and Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region—as well as Nepal. The expressway traffic mileage across the region is 123,300 kilometers, including 467.98 kilometers of expressways and 73,800 kilometers of rural roads.

Traffic map of the Xizang Autonomous Region
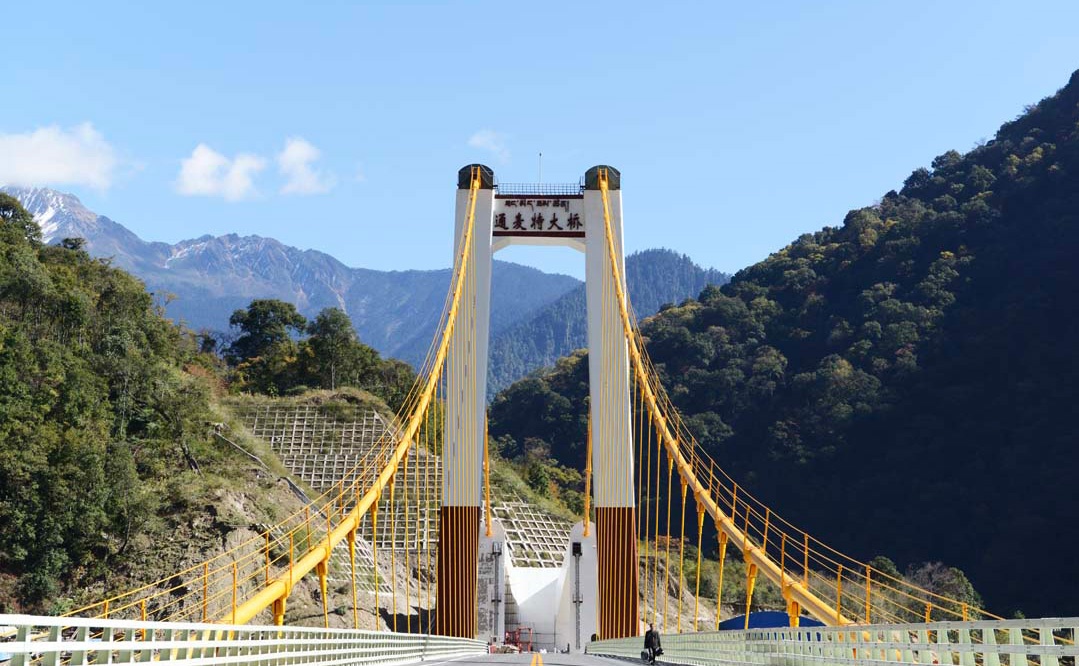 Throat project of Sichuan-Xizang section on G318—Tangmai Bridge |
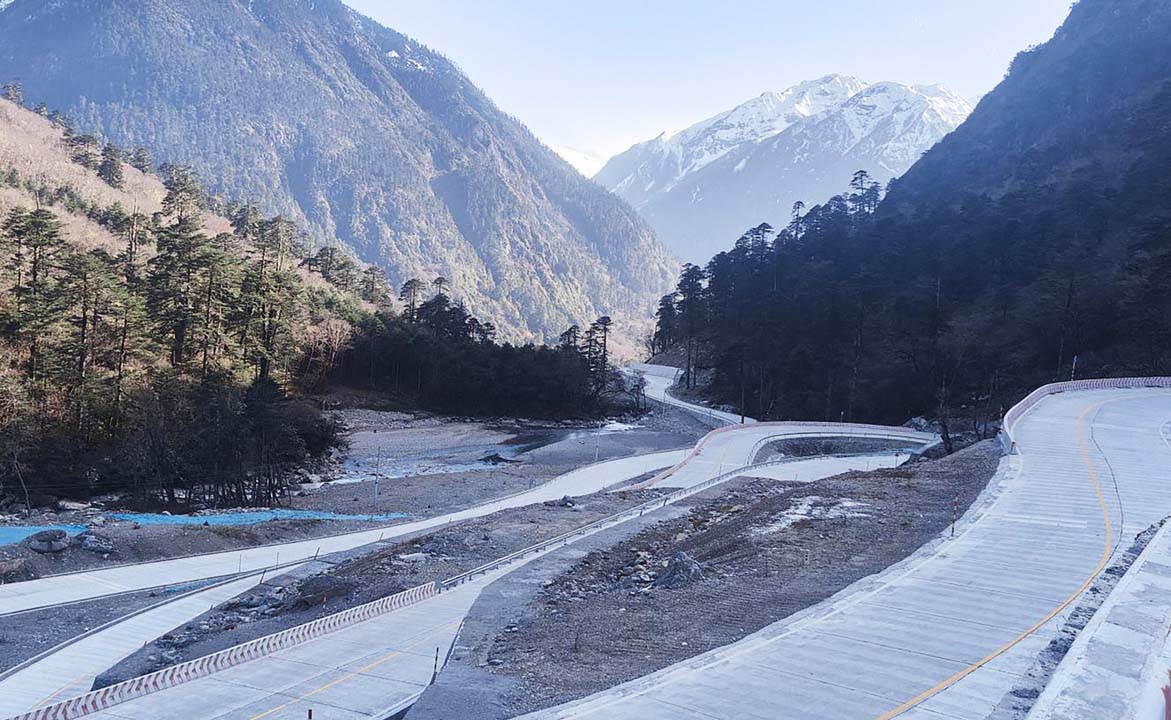 Metog-Dzayul section of reconstructed G219 |
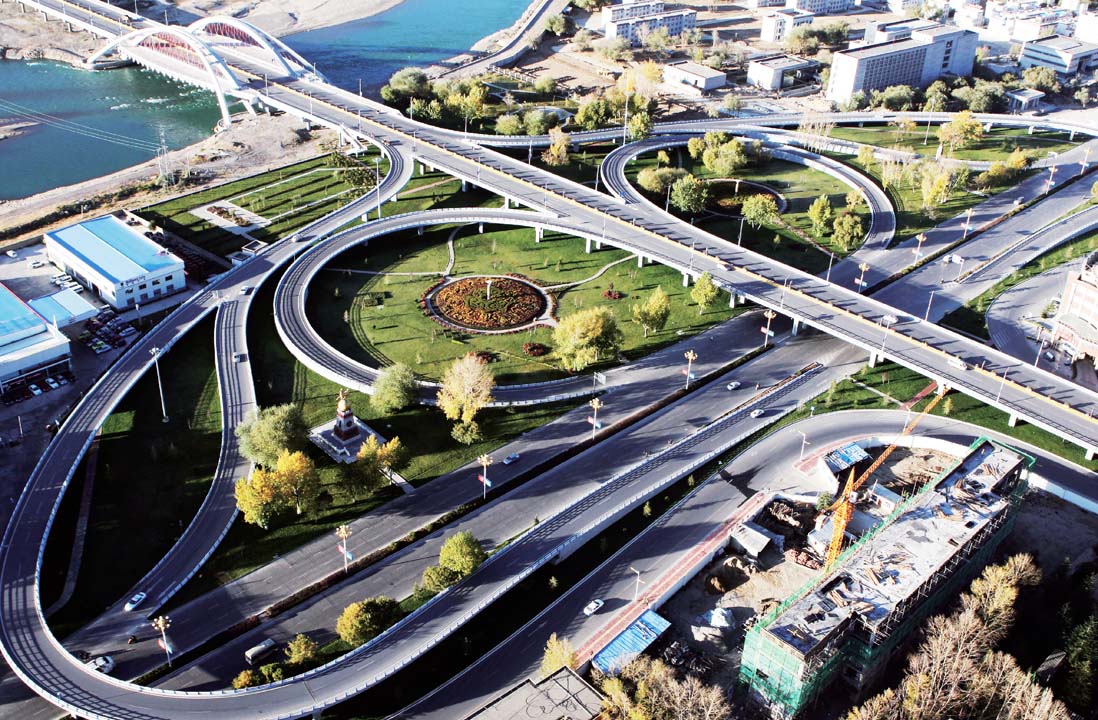 The first modern large-scale overpass in Xizang's history—Liuwu Bridge in Lhasa |
 Gongkar–Zêtang High-grade Highway |
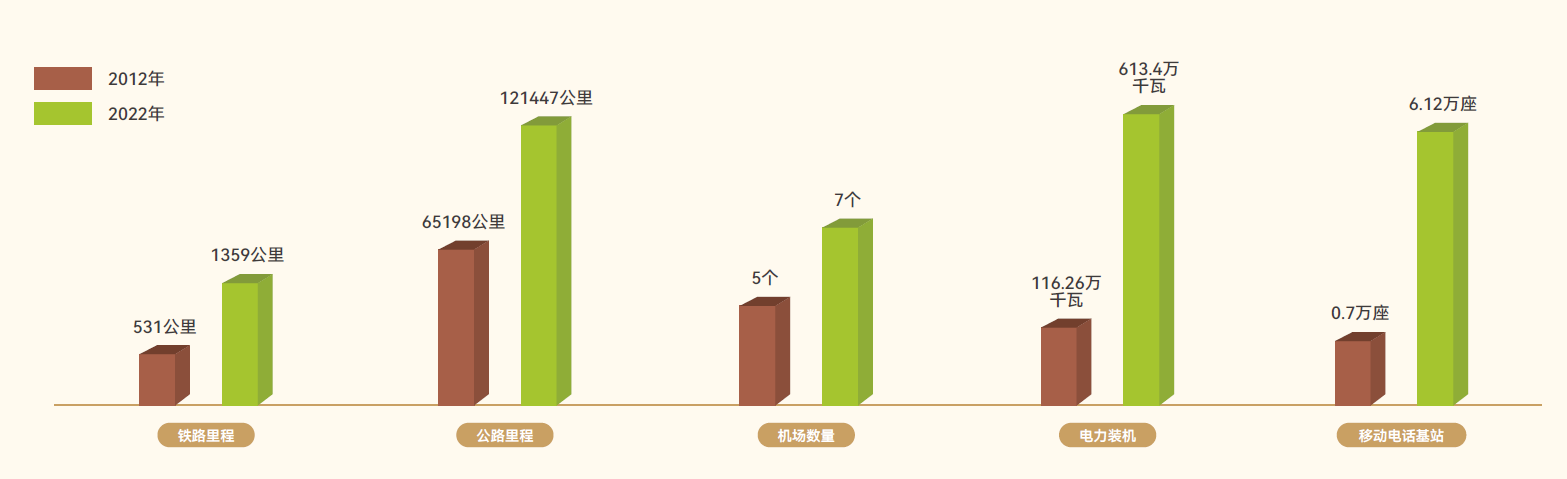 Comparison of railway mileage, expressway mileage, number of airports, installed power capacity, and number of mobile phone base stations in Xizang in 2012 and 2022 |
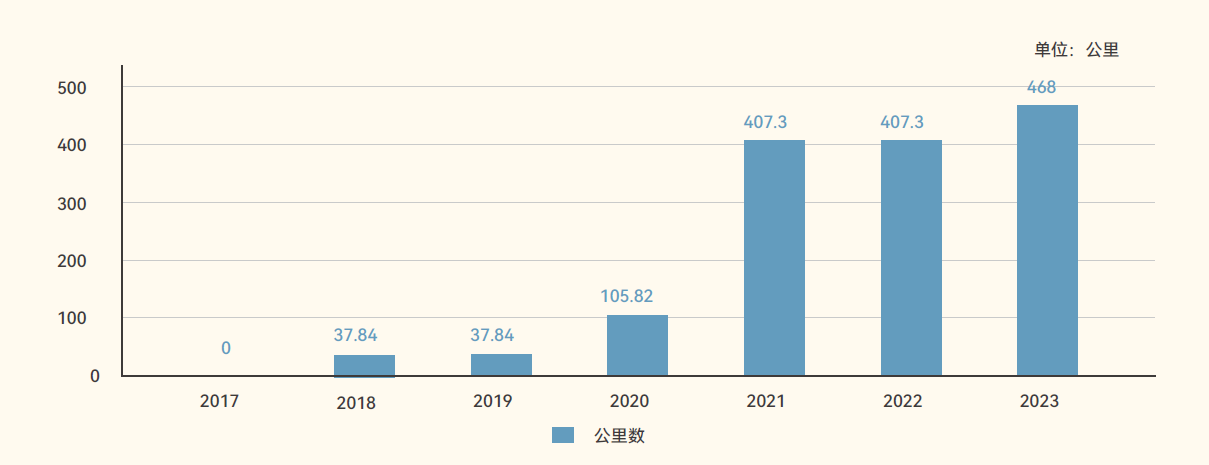 Change of expressway mileage in 2017-2023 |
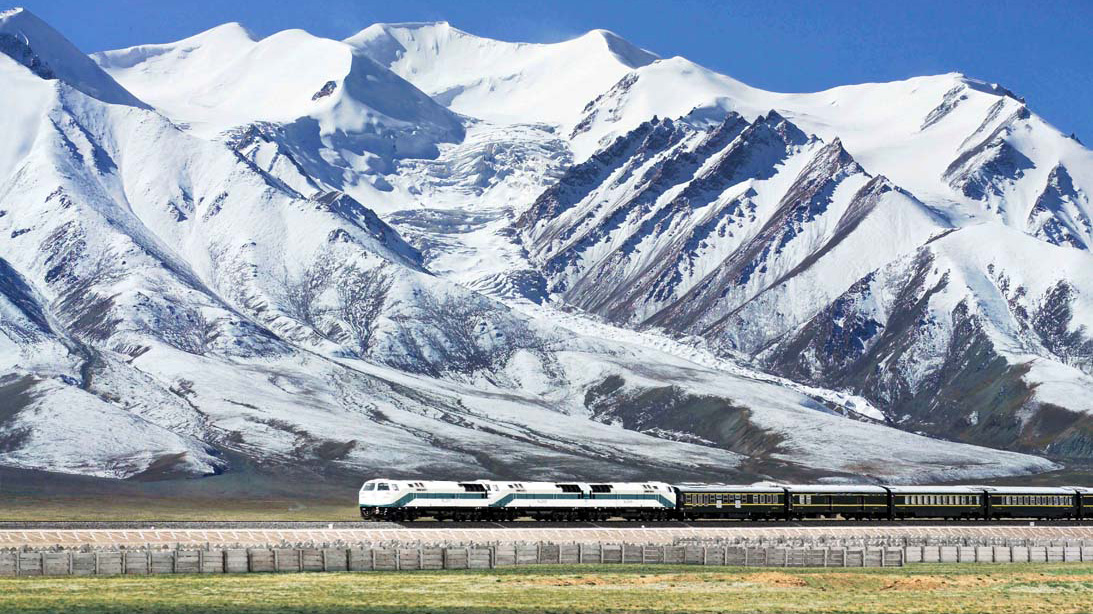
By the end of 2023, Xizang's railway operating mileage reached 1,359 kilometers, nearly double the length recorded in 2012. Lhasa, Lhoka, Nagqu, Shigatse, and Nyingchi have achieved trunk railway connections. In July 2006, the completion and opening of the Golumd-Lhasa section of the Qinghai-Xizang Railway marked a milestone in the history of human railway construction. In August 2014, the Lhasa-Shigatse Railway was completed and opened, alleviating the region's dependence solely on highway transportation in southwest Xizang. In June 2021, the Lhasa-Nyingchi section of the Sichuan-Xizang Railway, the first electrified railway, was completed and opened half a year ahead of schedule, marking the end of the era without railway service in southeast Xizang. This region is now accessible by Fuxing high-speed trains. In November 2020, construction officially began on the Ya'an-Nyingchi section of the Sichuan-Xizang Railway, a century-old strategic project.
 In July 2006, the Golumd-Lhasa section of the Qinghai-Xizang Railway was completed and opened to traffic |
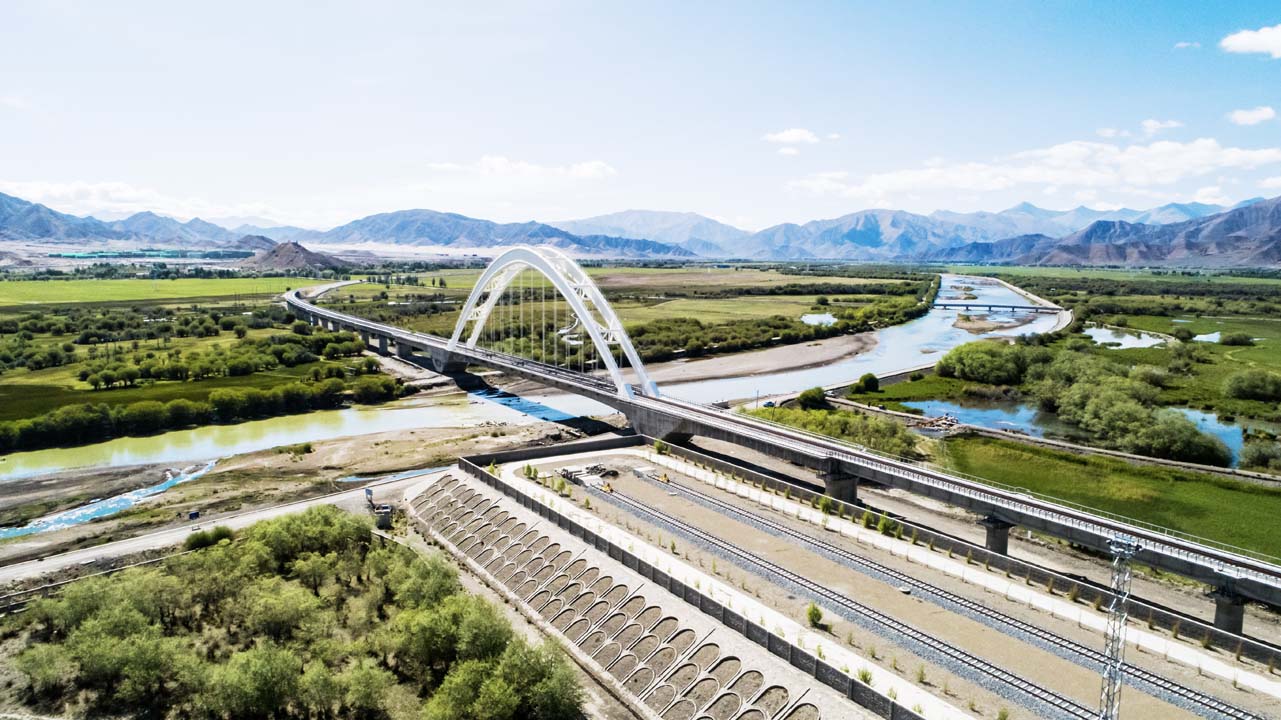 In August 2014, the Lhasa-Shigatse Railway was completed and opened to traffic |
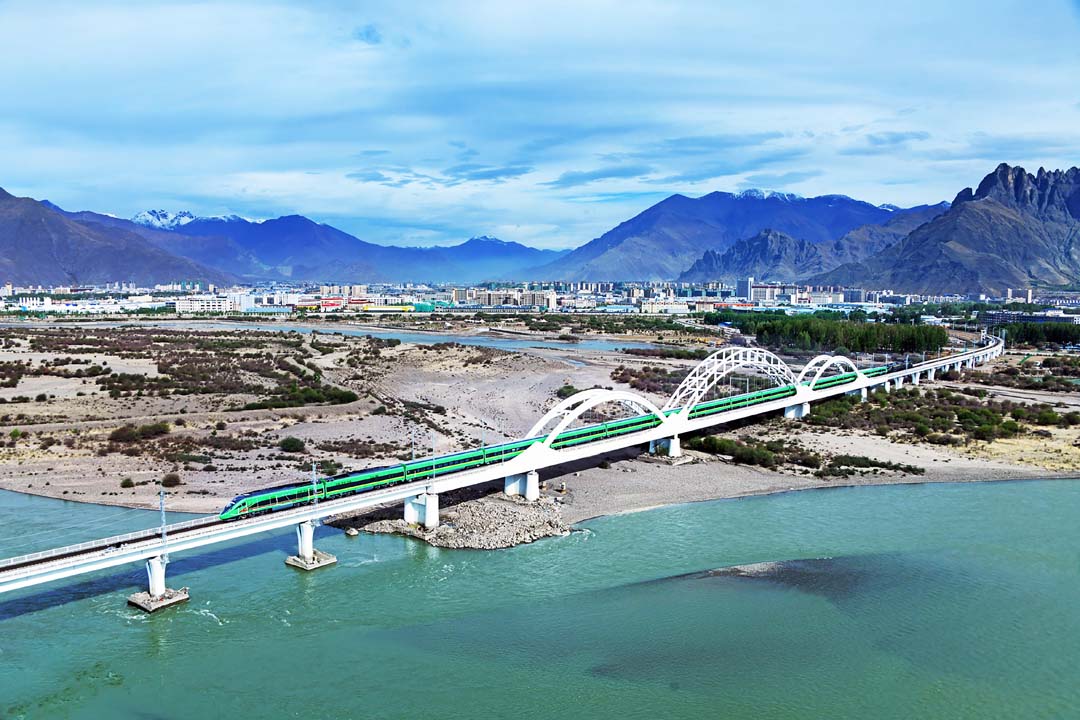 In June 2021, the Lhasa-Nyingchi section of the Sichuan-Xizang Railway, the first electrified railway in Xizang, was completed and opened to traffic |
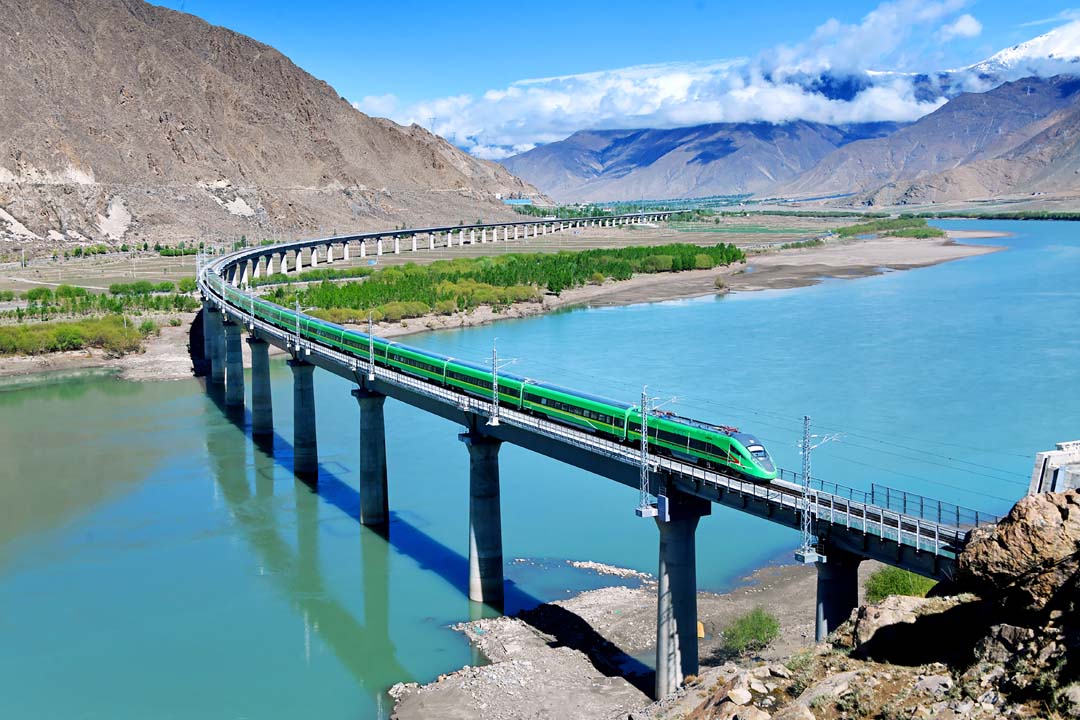 Fuxing high-speed trains (power-concentrated bi-mode multiple units) pass through the major bridge over the Yarlung Zangbo River in Sangri County. |
Since the 18th CPC National Congress, Xizang's aviation infrastructure has seen rapid development. The "1+7" transport airport layout, with Lhasa Gongkar Airport as the main hub and Bangda, Mainling, Gunsa, Heping, Lhunze, Dingri, and Burang airports as feeder airports, has been established. To date, a total of 174 air routes connecting 74 cities have been opened, showing an increase of 137 new air routes and 67 more navigable cities compared to 2011.
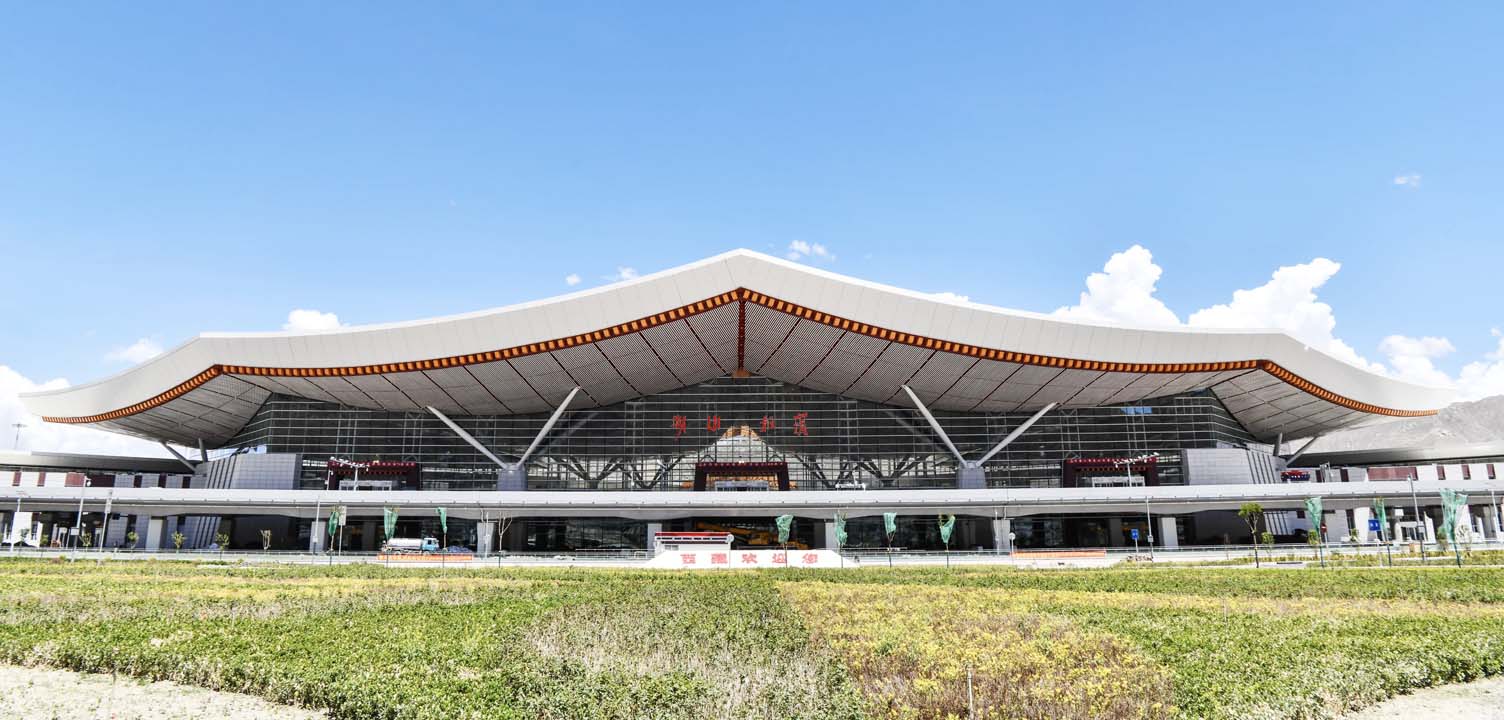

New terminal of Lhasa Gongkar Airport after renovation
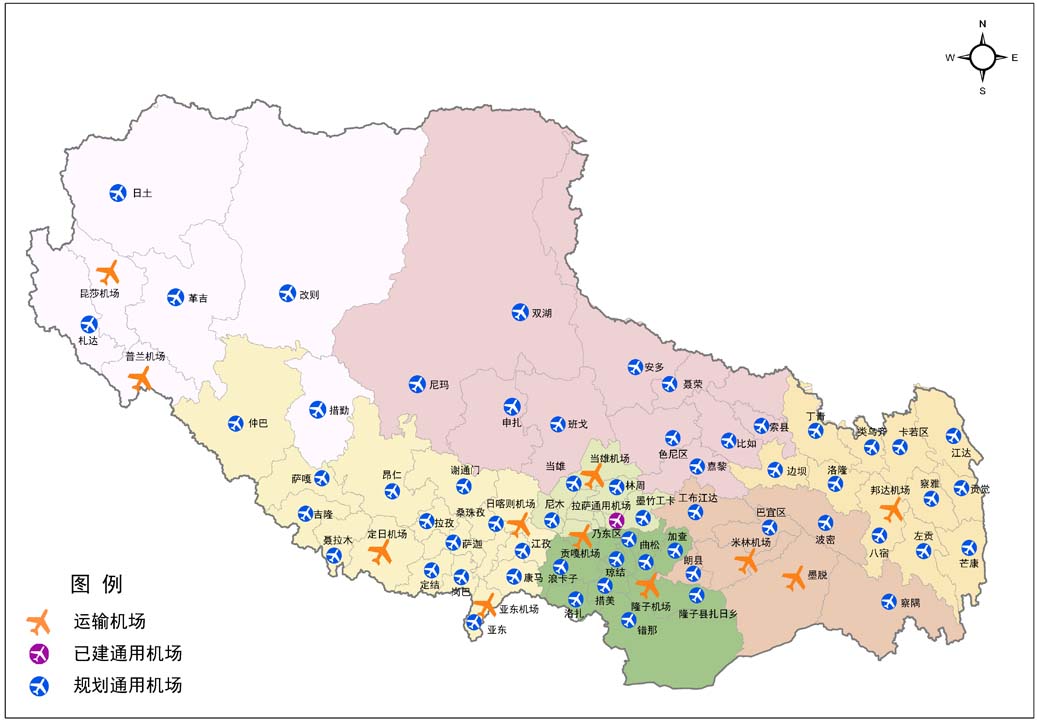 Layout of civil aviation "1+7" transport airports |
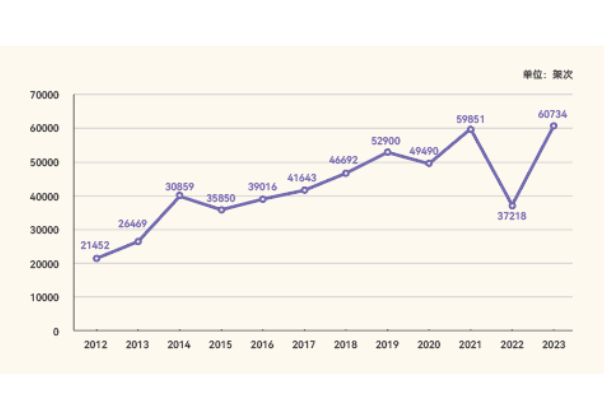 Civil aviation landing and take-off chart |
 New appearance of Ngari Burang Airport after renovation |
 In December 2022, Shigatse Dingri Airport was opened to air traffic |
 In December 2023, the new second runway of Lhasa Gongkar Airport was officially put into operation. |
Make progress in water conservancy facilities
Key water conservancy projects such as Pondo, Lalho, and Xianghe are now operational. The development of urban and rural flood control embankments has been expedited, leading to the establishment of a versatile water conservancy system integrating flood control, irrigation, water supply, power generation, ecological preservation, tourism, and other essential services.
 Suwalong Hydropower Station |
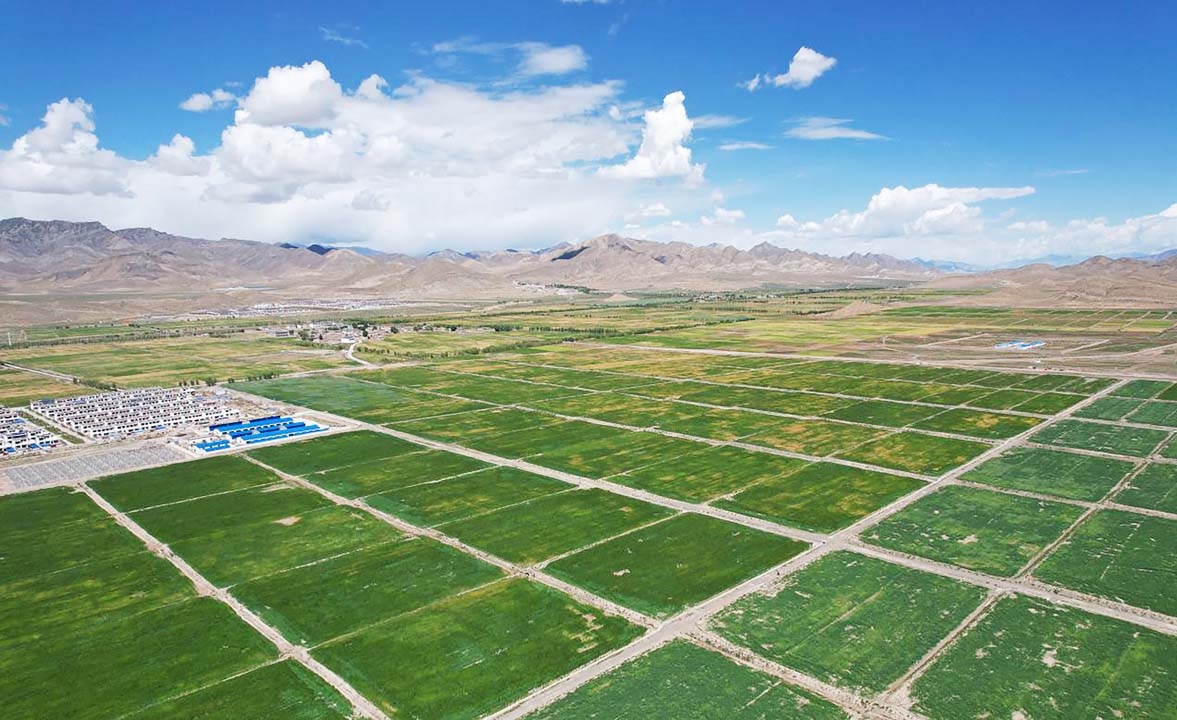 Irrigation area of Lalho Water Conservancy Project |
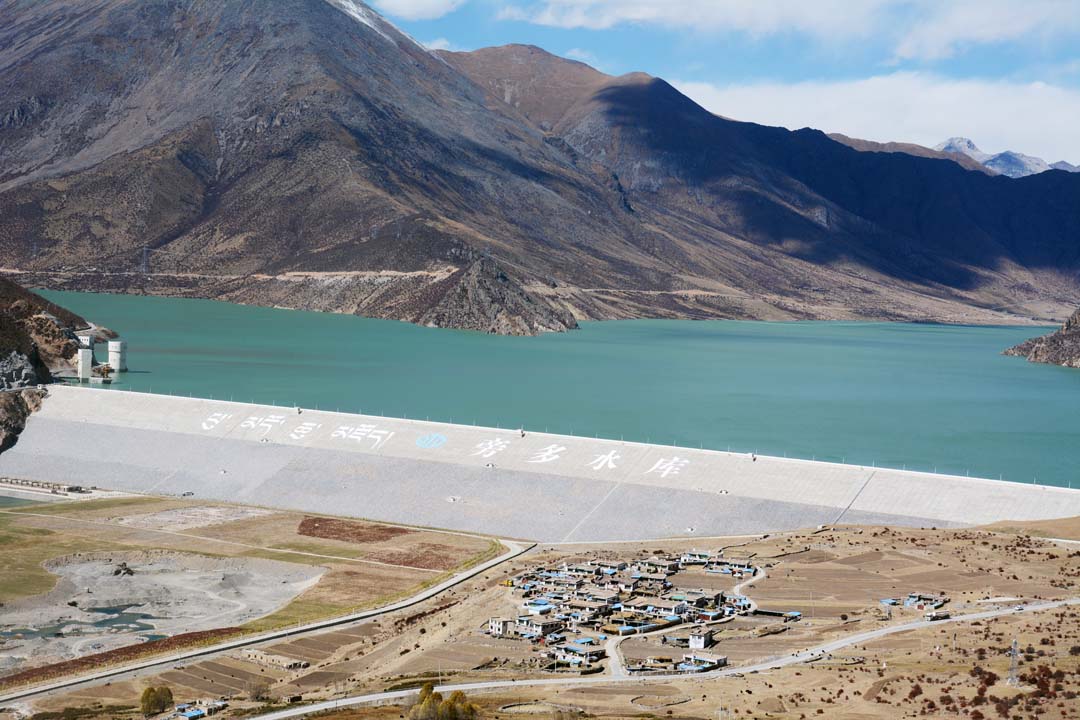 Pondo Water Conservancy Project |
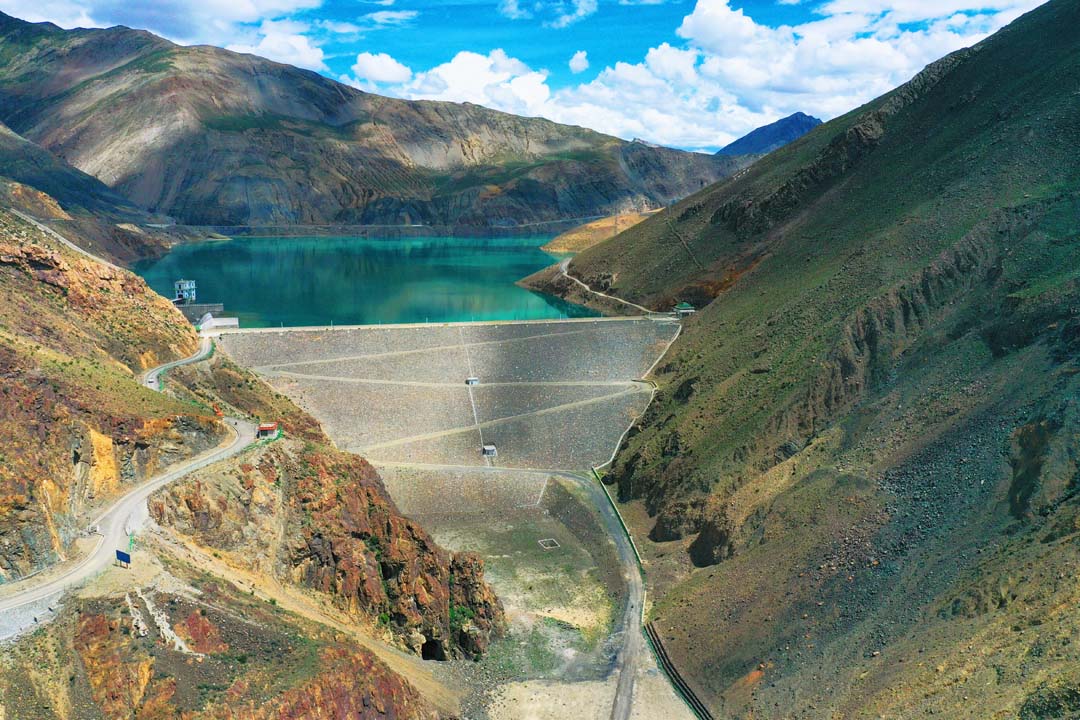 Manla Reservoir |
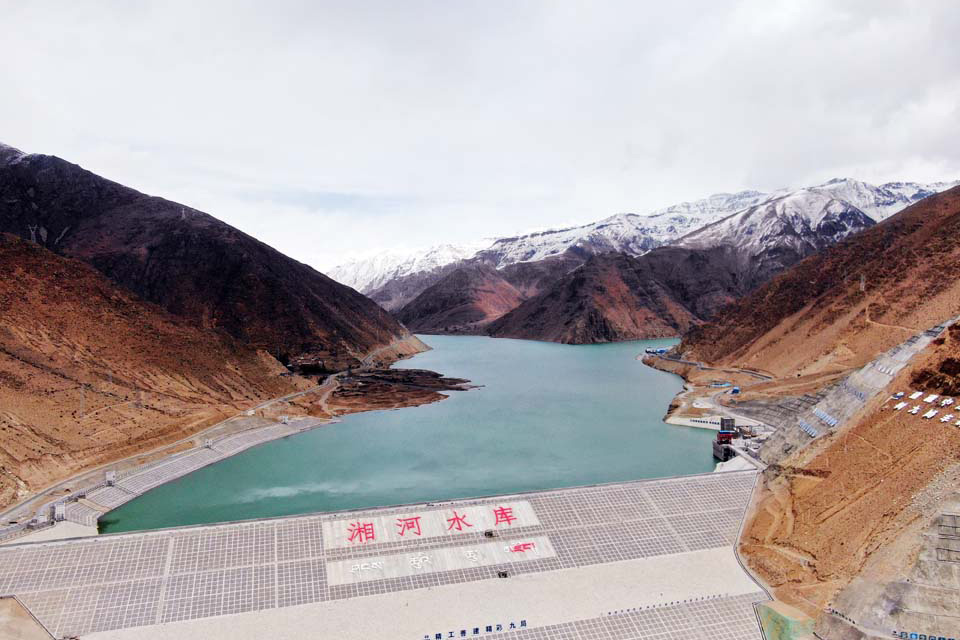 Xianghe Reservoir |